Asynchronous Collaborative Autoscanning with Mode Switching for Multi-Robot Scene Reconstruction |
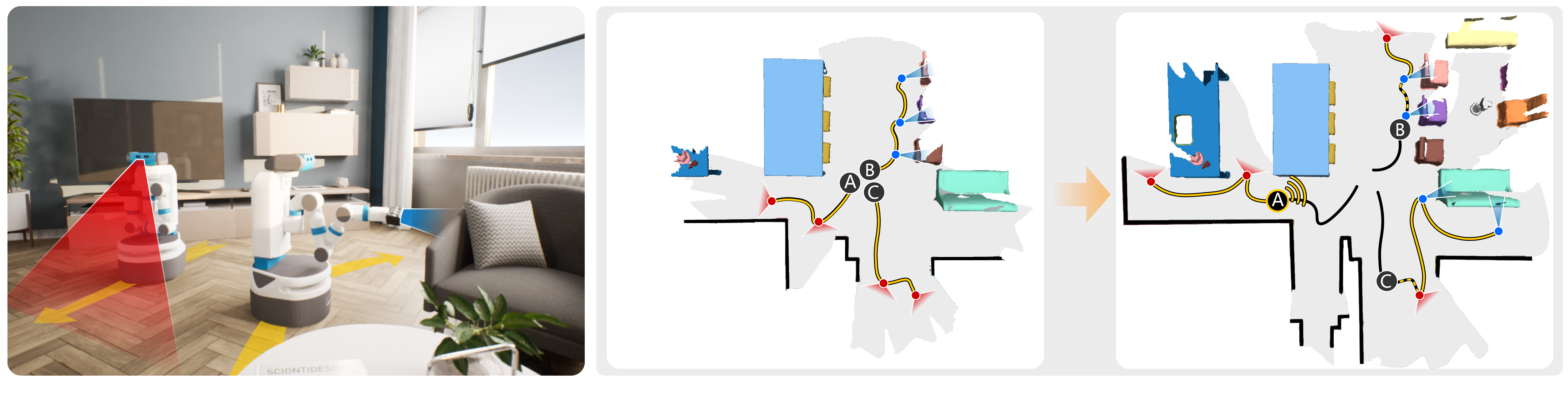
Figure 1: (Left) Two scanning modes: explorer mode with rapid moving speed and far vision (shown in red) for exploration task and reconstructor mode with low moving speed and narrow vision (shown in blue) for object reconstruction task; (Middle & Right) Our asynchronous collaborative autoscanning method: given the initially reconstructed scene by turning the three robots around their initial locations, our method first generates a set of tasks with the yellow path for each robot (middle). Once one robot has completed all its assigned tasks, robot A in this case, new tasks will be generated and appended to all the robots immediately (right). The completed paths are shown in black, and the paths assigned in the previous round but haven't been completed are shown with dashed yellow lines on top of the black.
Abstract
When conducting autonomous scanning for the online reconstruction of unknown indoor environments, robots have to be competent at exploring the scene structure and reconstructing objects with high quality. Our key observation is that different tasks demand specialized scanning properties of robots: rapid moving speed and far vision for global exploration and slow moving speed and narrow vision for local object reconstruction, which are referred as two different scanning modes: scout and raider, respectively. When further requiring multiple robots to collaborate for efficient exploration and fine-grained reconstruction, we study the questions on when to generate and how to assign those tasks. Therefore, we propose a novel asynchronous collaborative autoscanning method with mode switching, which generates two kinds of scanning tasks with associated scanning modes, i.e., exploration task with scout mode and reconstruction task with raider mode, and assign them to the robots to execute in an asynchronous collaborative manner to highly boost the scanning efficiency and reconstruction quality. Those generated tasks are assigned to the robots by solving a modified Multi-Depot Multiple Traveling Salesman Problem (MDMTSP). Moreover, to further enhance the collaboration and increase the efficiency, we propose a task-flow model that actives the task generation and assignment process immediately when any of the robots finishes all its tasks with no need to wait for all other robots to complete the tasks assigned in the previous iteration. Extensive experiments have been conducted to show the importance of each key component of our method and the superiority of our method over previous methods in scanning efficiency and reconstruction quality.Download
paper(~30M)supplementary material(~3M)
Code (coming soon)
Slide (coming soon)
Video
Talk
The video will be uploaded after the conference.Results

Figure 2: Reconstruction error difference between the method of [Dong et al. 2019] and our method. Red indicates a higher reconstruction error of [Dong et al. 2019] compared to ours while blue indicates similar reconstruction quality.

Figure 3: Comparison of the task scheduling between two settings of our method with (Ours) and without the asynchronous task-flow model (NoFlow). All robots switch between the explorer mode (red) and reconstructor mode (blue), and each time when the control center is activated for new task generation and assignment is indicated by the black dotted line. Comparing to our method, the robots in NoFlow have idle time (shown in black slash region) to wait for others finishing all assigned tasks, which leads to significant time waste during the whole process.
Acknowledgments
We thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments. This work was supported in parts by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61872250, 62025207), Guangdong Natural Science Foundation (2021B1515020085), Shenzhen Science and Technology Program (RCYX20210609103121030), and Guangdong Laboratory of Artificial Intelligence and Digital Economy (SZ).
Bibtex
| @ | article{ | Guo-2022-AsyncScan, | |
| title | = | {Asynchronous Collaborative Autoscanning with Mode Switching for Multi-Robot Scene Reconstruction}, | |
| author | = | {Junfu Guo, Changhao Li, Xi Xia, Ruizhen Hu, Ligang Liu}, | |
| journal | = | {ACM Transactions on Graphics (SIGGRAPH Asia 2022)}, | |
| volume | = | {41}, | |
| number | = | {6}, | |
| pages | = | {198:1 -- 198:13}, | |
| year | = | {2022}} |